The Ultimate Beginner's Guide to Interpreting Nuclear Heart Scan Resul…

Shanon
2025-04-23 03:49
57
0
본문
 Interpreting the results of a non-invasive nuclear heart scan, also known as a myocardial perfusion scan, can be perplexing for those who are not familiar with vascular medicine. This is a comprehensive guide for beginners to grasp the process and what to look forward to from the results.
Interpreting the results of a non-invasive nuclear heart scan, also known as a myocardial perfusion scan, can be perplexing for those who are not familiar with vascular medicine. This is a comprehensive guide for beginners to grasp the process and what to look forward to from the results.A nuclear heart scan is a cardiovascular test used to investigate blood flow to the heart muscle. During the test, a small amount of radioactive material, known as a tracer, is injected into the bloodstream. The tracer emits signals, which are detected by a sophisticated camera, showing the heart's efficiency and blood flow patterns.
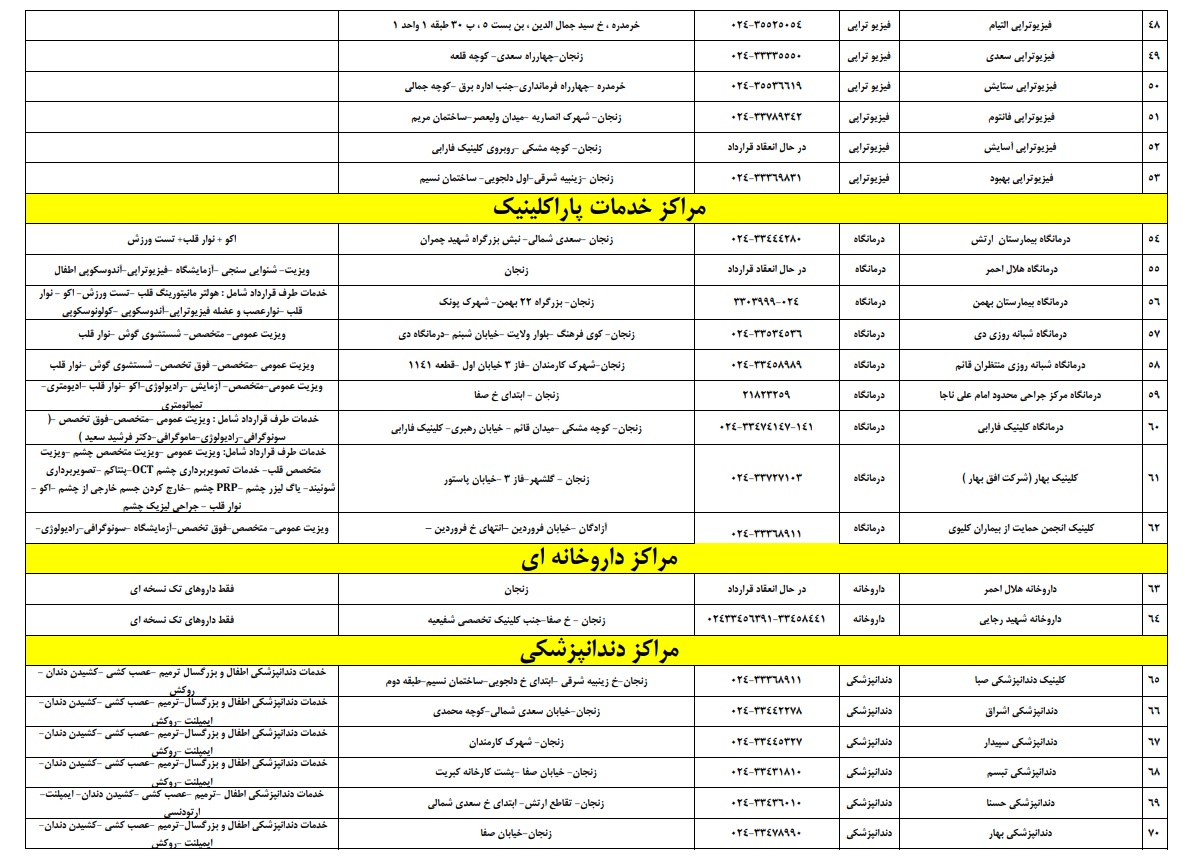
The test has three main objectives: to identify coronary artery disease, to assess the extent of damage from a heart attack, and to evaluate the success of treatment. In a nuclear heart scan, the right coronary artery, left coronary artery, and circumflex artery are typically assessed.
After the test is completed, the results are interpreted based on several parameters. The images generated during the test are divided into several segments, each representing a specific portion of the heart muscle. These images are then evaluated to determine if there are any signs of reduced blood flow, indicating possible coronary artery disease.
In a typical nuclear heart scan, the results are classified into several categories, including normal, moderately abnormal, moderately abnormal, and severely abnormal. In a normal test, all divisions of the heart muscle receive adequate blood flow. A severely abnormal test indicates that some areas of the heart muscle receive reduced blood flow, but it may not necessarily indicate coronary artery disease.
A severely abnormal test shows that significant regions of the heart muscle receive inadequate blood flow, which may be an sign of coronary artery disease. In a severely abnormal test, the majority of the heart muscle does not receive adequate blood flow, indicating severe coronary artery disease.
In addition to the general evaluation, the nuclear heart scan may also indicate on various other conditions, such as a temporary ischemic dilation (TID), اسکن قلب where the heart muscle appears to have expanded during the test, suggesting a possible blockage. A low ejection factor or left ventricular function may also be stated, indicating that the heart is not pumping efficiently.
In general, a normal nuclear heart scan result is encouraging, indicating that the heart muscle is receiving adequate blood flow and cardiac function is normal. A mildly abnormal result may require further testing, such as stress tests or cardiac catheterization, to determine the extent of coronary artery disease.
In conclusion, a nuclear heart scan is a valuable test for assessing heart function and diagnosing coronary artery disease. Understanding the results of the test requires a basic knowledge of cardiology and analyzing various parameters. If you have undergone a nuclear heart scan, it is crucial to discuss your results with a healthcare professional to understand the consequences for your heart health.
When receiving your results, you should attentively close attention to the following considerations:
- Your blood vessels and the extent of blockage
- The presence of transient ischemic dilation
- Your ejection factor or left ventricular function
- Your general heart health and any suggestions from the doctor
댓글목록0
댓글 포인트 안내